Understanding Lock Functions
Understanding Lock Functions can be a daunting task, especially with the multitude of options available in the market today. With over 50 different lock functions to choose from, it can be difficult to remember how each one works. However, when it comes to specifying locks, the majority of them fall into just six mechanical lock functions. Having a comprehensive understanding of these common functions, along with a basic understanding of electromechanical locks and deadbolt functions, is essential for determining which lock function is appropriate for each door. In this article, we will provide an overview of the most common functions for mechanical locks, highlighting their features and typical applications. By the end, you will have a better understanding of which lock function to choose for your specific needs, striking the balance between life safety and security concerns.

Essentials of Lock Functions
Definition and Importance
Lock functions refer to the different ways in which a lock can be operated and the level of security it provides. The importance of lock functions lies in ensuring both safety and security in various settings, such as schools, offices, homes, and industrial facilities. Selecting the appropriate lock function is crucial for maintaining the balance between life safety and security concerns.
The Evolution of Lock Functions
Lock functions have evolved over time as the need for enhanced security and convenience has grown. From simple mechanical locks to more advanced electromechanical locks, the options for securing doors have become increasingly complex. Today, manufacturers offer a wide range of lock functions, with each serving specific purposes and meeting different security requirements.
Mechanical vs. Electromechanical Locks
Mechanical locks operate solely through mechanical mechanisms, such as keys and levers, while electromechanical locks combine mechanical components with electronic features. Mechanical locks are commonly used and offer reliable security. On the other hand, electromechanical locks provide additional functionalities, such as integration with access control systems and remote monitoring capabilities.
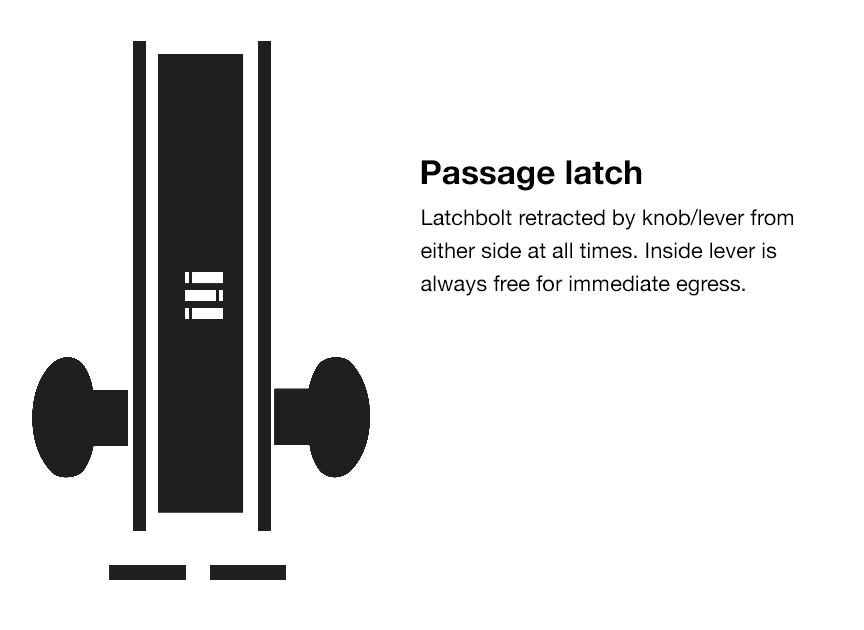
Passage Locks
Functionality and Use Cases
Passage locks are designed for doors that do not need to be locked, allowing free egress at all times. They do not have a key cylinder or any means to lock the door. These locks are commonly used in areas such as hallways, closets, and communal spaces where security is not a major concern, but easy access is desired.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing a passage lock is relatively straightforward. It typically involves mounting the lockset on the door and ensuring proper alignment with the strike plate on the door frame. Maintenance for passage locks mainly involves periodic cleaning and lubrication of the internal components to ensure smooth operation.
Common Applications
Passage locks find extensive use in both residential and commercial settings. In residences, they are commonly installed on interior doors, such as bedroom doors and bathroom doors, where privacy is not a major requirement. In commercial buildings, passage locks are often used on doors leading to common areas, such as conference rooms and break rooms.
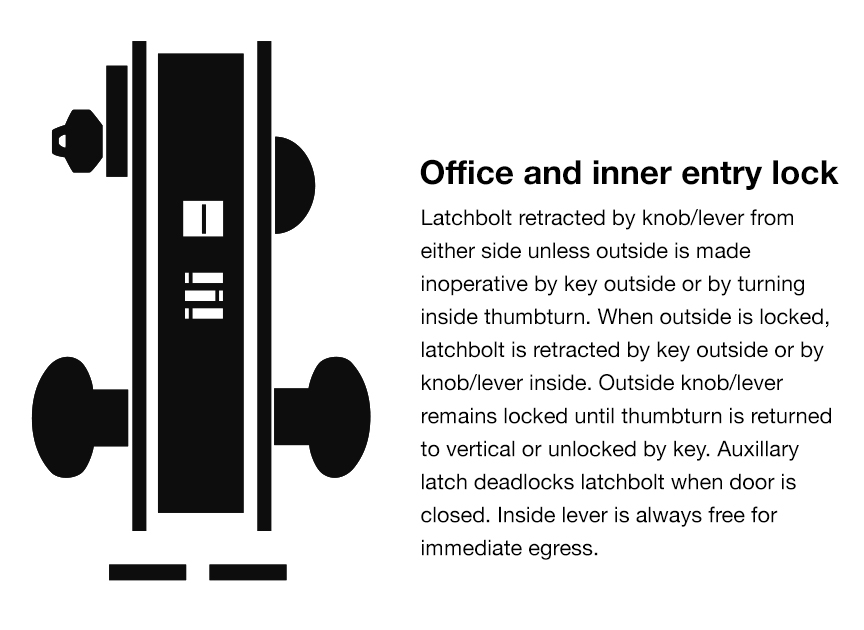
Privacy Locks
Key Features and Design
Privacy locks are designed for areas where privacy is essential, such as single-occupant restrooms or dressing rooms. These locks allow the door to be locked from the inside using a thumbturn or a push button/turn mechanism, providing privacy for the occupant. The lock can usually be unlocked from the outside using a tool, rather than a key.
Variations and Enhancements
There are several variations of privacy locks to suit different environments and requirements. For example, hospital privacy locks feature a thumbturn on both the inside and outside to allow quick access for hospital staff. Some privacy functions also incorporate an indicator to visually display the locked or unlocked status of the door.
Operational Mechanism
Privacy locks operate using a latch mechanism that can be engaged or disengaged by turning the thumbturn or pushing the button/turn mechanism. When locked, the latch engages with the strike plate, preventing the door from being opened without the proper unlocking action.
Storeroom Locks
Purpose and Security Level
Storeroom locks are designed to provide a higher level of security. The outside lever remains locked at all times, requiring a key to retract the latchbolt and open the door. Once the key is removed, the door automatically locks on the outside, ensuring restricted access to the designated area. Storeroom locks offer enhanced security for storage rooms or areas where valuables are kept.
Key Operation and Access Control
The key is used to operate the locking mechanism of a storeroom lock. When the key is inserted and turned, the latchbolt retracts, allowing the door to open. Removing the key automatically engages the latchbolt, rendering the outside lever inaccessible without a key. Storeroom locks can be beneficial for controlling access to sensitive materials or equipment.
Suitable Locations for Use
Storeroom locks are commonly installed in areas that require strict access control, such as server rooms, supply closets, and utility rooms. These locks ensure that only authorized personnel with the appropriate key can gain entry, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or theft.
Classroom Locks
Design for Safety and Accessibility
Classroom locks are specifically designed to enhance safety and security in educational settings. They are typically equipped with features that allow teachers to quickly secure the classroom during a lockdown event. Classroom locks should also comply with accessibility standards to ensure ease of use for everyone, including individuals with disabilities.
Lockdown Mode Features
Classroom locks often have a lockdown mode feature that allows teachers to easily and swiftly secure the door from the inside in case of an emergency. This feature typically involves a thumbturn or a push button/turn mechanism that can quickly engage the lock. Some locks may also include indicators to show whether the door is locked or unlocked.
Advantages in Educational Settings
Classroom locks provide peace of mind for both teachers and students by enhancing safety in educational environments. In emergency situations, quick and reliable access control can significantly reduce response time and protect individuals within the classroom. Additionally, these locks can help maintain an effective lockdown strategy during potential threats.
Deadbolt Locks
Types and Mechanisms
Deadbolt locks are known for their strength and resistance against forced entry. There are two main types: single-cylinder deadbolts and double-cylinder deadbolts. Single-cylinder deadbolts are operated with a key from the outside and a thumbturn on the inside, while double-cylinder deadbolts require a key for operation on both sides.
Installation Guidelines
Installing a deadbolt lock requires proper alignment and reinforcement of the door and door frame. The lock should be positioned in a way that the bolt fully extends into the strike plate when locked. Additionally, reinforcing the strike plate and the door frame can enhance the overall security provided by the deadbolt lock.
Security Benefits
Deadbolt locks offer enhanced security compared to other types of locks due to their robust construction and resistance to physical attacks. The extended bolt of a deadbolt lock provides added strength and prevents the door from being easily forced open. They are commonly used on exterior doors to ensure a high level of protection against break-ins.
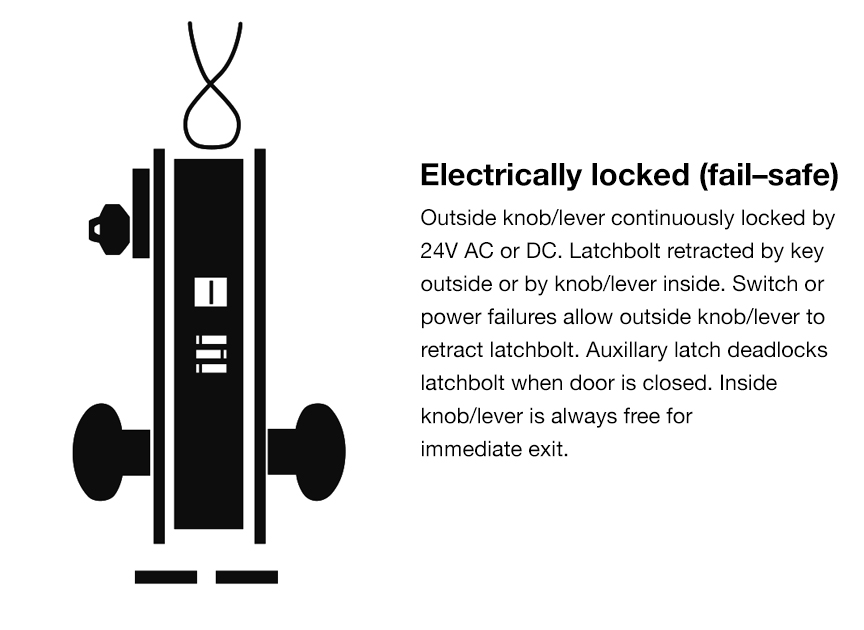
Electromechanical Locks
Integration with Access Control Systems
Electromechanical locks combine mechanical locking mechanisms with electronic components. They can be integrated into access control systems, allowing for centralized management and monitoring of access to secured areas. This integration enables features such as remote unlocking, time-based access restrictions, and audit trails.
Power Sources and Fail-Safe/Fail-Secure Options
Electromechanical locks typically require a power source, such as batteries or direct electrical wiring. They can be designed as either fail-safe or fail-secure. Fail-safe locks automatically unlock during power outages, ensuring safe egress, while fail-secure locks remain locked in the event of power failure, offering increased security.
Future Trends in Lock Technology
Lock technology is continually evolving to meet the demands of modern security challenges. One notable trend is the integration of smart lock features, allowing locks to be controlled remotely using smartphones or other connected devices. Additionally, advancements in biometric technology are being incorporated into lock systems, providing an additional layer of security through fingerprint or iris recognition.

Emergency Exit Devices
Compliance with Life Safety Codes
Emergency exit devices, also known as panic bars or crash bars, are essential for ensuring swift and safe egress during emergencies. These devices must comply with relevant life safety codes and standards to ensure that occupants can quickly and easily exit a building in case of a fire or other emergency situation.
Types and Applications
Emergency exit devices come in various types, including rim exit devices, mortise exit devices, and vertical rod exit devices. The choice of device depends on factors such as the type of door and the level of security required. These devices are primarily installed on exit doors to provide a means of rapid evacuation.
Maintenance Requirements
Proper maintenance of emergency exit devices is crucial to ensure their reliability and functionality during emergencies. Regular inspections and testing should be conducted to identify any issues or malfunctions. Basic maintenance tasks include cleaning, lubrication, and checking for loose or damaged parts.

Lock Function Selection Guide
Determining the Appropriate Lock Function
Selecting the right lock function for a specific application requires careful consideration of factors such as the level of security needed, access control requirements, and the intended use of the door. Consulting with security professionals and door hardware consultants can help in determining the most suitable lock function for a particular setting.
Considerations for Specific Environments
Different environments may have unique requirements when it comes to lock functions. For example, educational settings may prioritize safety features and ease of use for teachers and students during lockdown events. Commercial buildings may focus on access control and integration with security systems. Considering the specific needs of each environment is essential in selecting the appropriate lock function.
Consulting with Security Professionals
When in doubt or faced with complex security requirements, consulting with security professionals is highly recommended. These experts have the knowledge and experience to assess the unique needs of a facility and recommend the most suitable lock functions. Their expertise can help ensure that the chosen lock functions provide optimal security and convenience.
Security and Technology Trends
Smart Locks and IoT Integration
The integration of smart lock features and Internet of Things (IoT) technology has revolutionized the lock industry. Smart locks allow users to control and monitor their locks remotely using smartphones or other connected devices. This functionality provides convenience, flexibility, and additional security features, such as real-time access notifications and temporary access codes.
Biometrics in Lock Systems
Biometric technology, such as fingerprint or iris recognition, is increasingly being integrated into lock systems. This advanced form of access control provides a high level of security, as biometric data is unique to each individual. Biometric locks offer convenience and eliminate the need for traditional keys or access cards, reducing the risk of unauthorized access due to lost or stolen credentials.
The Future of Lock Security
The future of lock security holds great potential for advancements in technology and innovation. With the continued development of IoT, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, locks may become even smarter and more interconnected. Enhanced encryption methods and biometric authentication are likely to play significant roles in securing our spaces, ensuring both safety and convenience.



